In this article, we talk about toothpaste, types, uses and its active contents. we also give some not-so-common fun ideas about it. with Special guest writing with Dr. Yasmine Kottait.

What is toothpaste really?
Toothpaste (either in a form of paste or gel) is generally used to clean and preserve the health and appearance of the oral cavity ( teeth, gums). It helps improve oral hygiene ( as an abrasive ) to remove plaque and food, helps prevent bad breath and prevents tooth decay and gum disease.
Whats the difference between Paste and Gel?
While the brand of gel and paste is important for helping you combat different kinds of oral health problems, there actually isn’t a huge difference between the gel and paste formulas. The most obvious differences are their physical appearance, tastes, and textures.
Gels
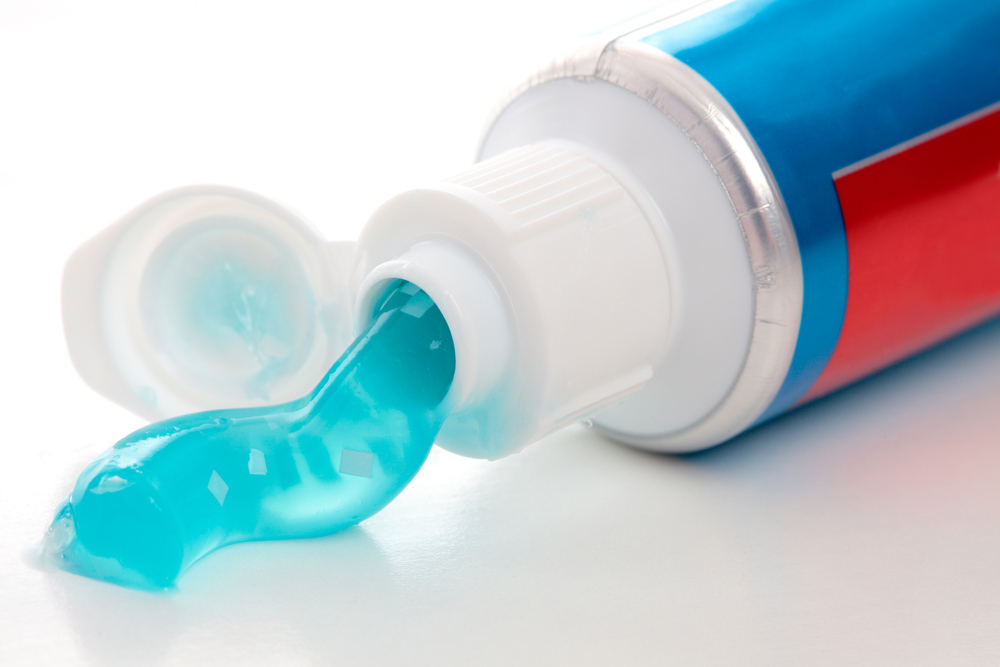 are made of silica to create a clear texture. When it comes to brushing, gels tend to be a bit less abrasive. You don’t get the nice foamy texture that you get from a paste. If you’re a messy brusher, then gels tend to create less of a spatter.
are made of silica to create a clear texture. When it comes to brushing, gels tend to be a bit less abrasive. You don’t get the nice foamy texture that you get from a paste. If you’re a messy brusher, then gels tend to create less of a spatter.
Pastes
are thicker in texture and tend to be a solid color. You can also get tri-colored pastes, green pastes, blue pastes, and even red. Pastes tend to go on your teeth thicker. Thusly, they can sometimes create a bit of a mess. I use a white paste, and since I use an electric toothbrush, I sometimes end up having to clean the foamy spray off of my bathroom mirror.
What are the functions toothpaste?
- Anti-decay / Anti-cavity toothpaste: This works with the availability of fluoride ( Sodium Fluoride (NaF), Stannous Fluoride (SnF2), or Monofluorophosphate (MFP2) etc.) as long as the fluoride content is 1,000 ppm (parts per million) or above. while the content is less for children at 500ppm fluoride and is usually flavoured, e.g. fruit flavour, candy flavour, which is more appealing to children.
- Whitening toothpaste: tend two distinctive parts of effectiveness:
- Surface stains (Physical): the use of stronger abrasives (silica) to help polish and remove surface
- Deep Stains (Chemical): like hydrogen peroxide to break down deeper stains.
These kind of toothpaste are effective for heavy smokers and coffee drinkers but long-term use of these kinds of toothpaste isn’t well known yet.
- Desensitizing toothpaste: these types of toothpaste relieves discomfort due to over-sensitive teeth to either hot or cold. The active ingredients actions are done via two mechanisms:
- Interrupting the neuron response to pain stimuli.
- Occluding the dentinal tubules of dentine.
Active ingredients such as Potassium Nitrate or Arginine, etc., are used by different product manufacturers.
- Anti-plaque toothpaste: This kind of toothpaste inhibits plaque accumulation, reduces the toxic effects of the bacterial toxin on the tooth surrounding tissues, thereby reduces the chances of getting gum disease. active ingredients for this action include Triclosan or Zinc Citrate, etc.
- Anti-calculus toothpaste: This type of toothpaste reduces the calcification of dental plaque thus prevent deposition of calculus. The active ingredient is Pyrophosphate or Zinc Citrate, etc.
Tooth Paste Contents
What do the active ingredients in toothpaste do?
- Sodium fluoride, stannous fluoride, and sodium monofluorophosphate: Evidence shows that toothpaste with higher
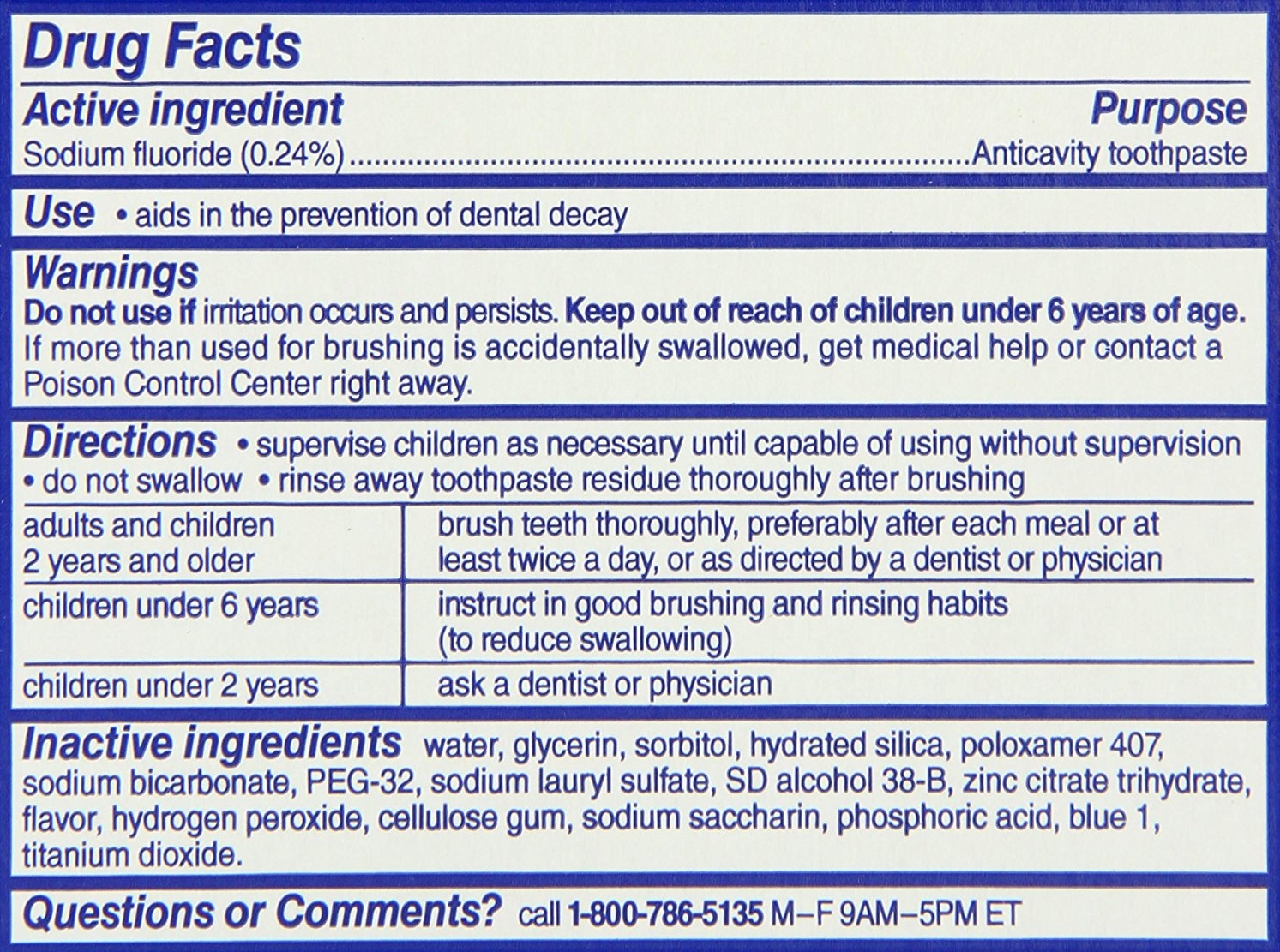
Toothpaste Active Ingredients – OziDent concentrations of fluoride are more effective at controlling decay, and help reduce the effect of acid erosion.
- Potassium nitrate, stannous fluoride, arginine and calcium sodium phosphosilicate (NovaMin): desensitizing agents with evidence of effectiveness in prevent sensitivity
- Triclosan, bromochlorophene zinc citrate, papain and sanguinaria extract: These are an anti-bacterial agent which reduces plaque, inflamed and bleeding gums, and decay.
- Arginine and calcium carbonate: These neutralize plaque acids, and help repair tooth enamel.
What about that additive in the toothpaste?
- An Abrasives: Hydrated silica, mica, sodium bicarbonate. They remove surface stains such as tea, coffee, and red wine.
- A binder: PVM/MA Copolymer A binder used with triclosan, so it stays on your teeth and gums.
- A Moisturizers and Humectants: Water, Sorbitol, glycerol, propylene glycol Humectants. They keep your toothpaste moist and prevents it from drying out.
- A detergent: Sodium Lauryl Sulfate (SLS), cocamidopropyl betaine and pentasodium triphosphate. A foaming detergent that dissolves dirt and grease and gives them a bubbles feeling.
- Antibacterial / Antifungal Agents: Methylparaben and sodium benzoate Preservatives that stop toothpaste bacteria growth.
- Thickeners: Cellulose gum, carrageenan and xanthan gum These thickeners provide texture and stop toothpaste from being too runny.
- Neutralizer: Sodium hydroxide Also known as lye and found it much larger quantities in drain and oven cleaner. It neutralizes the pH of other ingredients.
- Coloring Agents: Titanium dioxide (CI 77891) This color pigment makes toothpaste whiter and brighter and more appealing.
- Flavors: (essential oils are known allergens = Limonene, cinnamal, peppermint oil), glycerine, sucralose, sorbitol, lota carrageenan, sodium saccharin, aroma, mint flavor۔ Artificial or added sweeteners and flavor providers which makes brusing a pleasant experience and masks the bad odor.
- Preservatives: to keep the toothpaste safe for a long period at room temperature.
- Other Ingredients: Peroxides and baking soda.
Are these ingredients dangerous? what about All-natural Toothpaste?
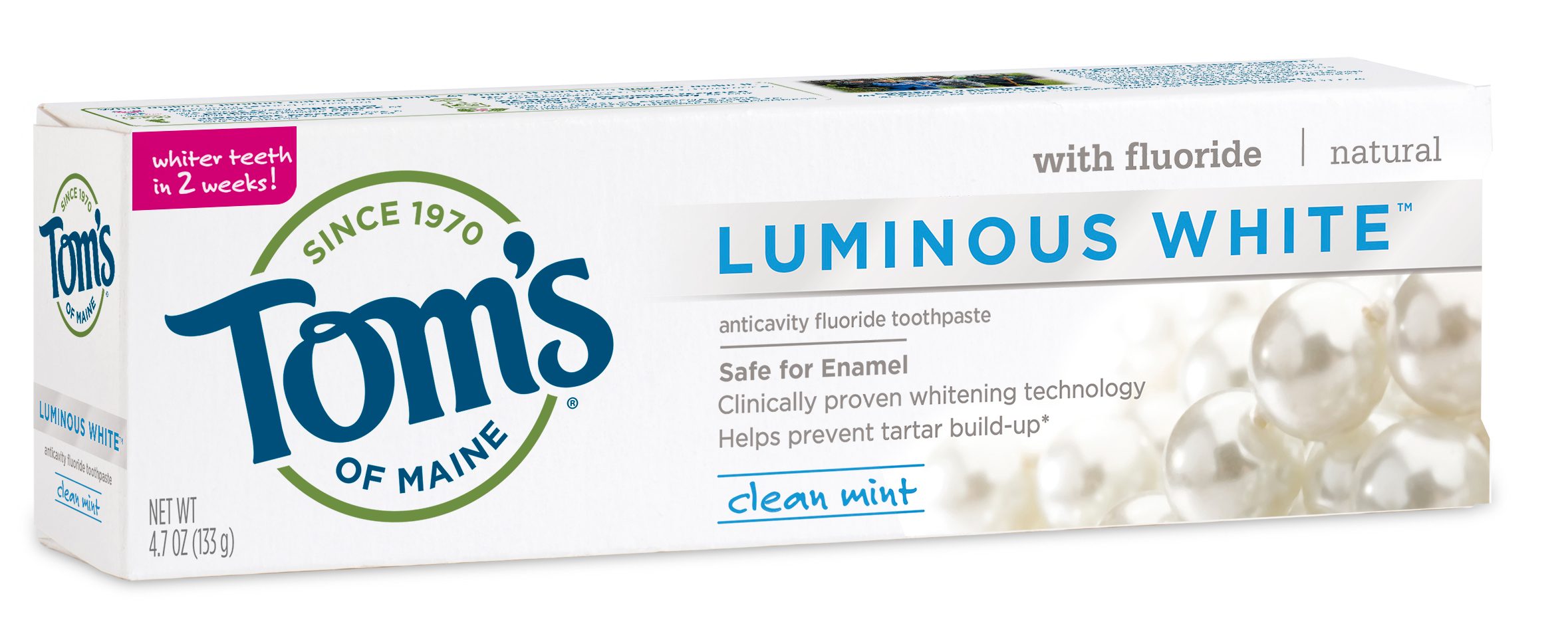

All Natural toothpaste: Companies such as Tom’s of Maine, among others, manufacture natural and herbal toothpaste and market them to consumers who wish to avoid the artificial ingredients commonly found in regular toothpaste. Many herbal kinds of toothpaste do not contain fluoride or sodium lauryl sulfate. The ingredients found in natural toothpaste vary widely but often include baking soda, aloe, eucalyptus oil, myrrh, plant extract (strawberry extract), and essential oils.

SLS Free Toothpaste: Some manufacturers have removed sodium lauryl sulfate, as there is limited evidence it causes skin irritation. For example, some people find that it is linked with mouth ulcers, and other people with the condition ‘dry mouth’ find it irritates the mouth, making the condition worse.
Does toothpaste for children and adult Differs?

Dr. Yasmine Kottait stated that it all comes down to the fluoride concentration when comparing the toothpaste for children and adults, in addition to the vast flavor choices the children toothpaste have to make it more appealing to children to brush.
Flouride is very healthy and beneficial for children teeth because it strengthens the teeth and prevents tooth decay. but because most young children can not master the art of spitting after brushing and just swallow the toothpaste. Those children who tend to swallow are in possible danger of fluoride toxicity if ingested toothpaste with high concentration aka adult toothpaste. That is why children toothpaste contains a lower concentration of fluoride to minimize the possibility of fluoride toxicity.

When choosing the proper toothpaste for Children, its important for the parent to decide on which toothpaste on appropriate amount of toothpaste based on the three age categories

Why does sweet Orange Juice taste so bitter after toothbrushing?

This is due to the action of sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS) or sodium lauryl ether sulfate (SLES). Which alter the taste. This is done by two actions.
- Inhibition of the ability to taste sweet.
- Breakdown of phospholipids that are naturally present in the mouth. phospholipids tend to soften the effect of food bitterness and as of such, without it, the taste of bitterness is increased.
Did you know that apples taste more pleasent after using toothpaste!!!
Should I rinse or should I not after Brushing my teeth with toothpaste?
A clinical trial that lasted for three years and included 407 children. It emphatically states:
Previous studies have indicated that rinsing the mouth with a beaker of water after toothbrushing may compromise the caries reducing effect of fluoride toothpaste.It is concluded that post-brushing rinsing with water, under the conditions of this study, does not significantly affect the caries reducing effect of a fluoride toothpaste.
Sources
- http://www.toothclub.gov.hk/en/en_adu_01_03_02_02.html
- https://www.webmd.com/oral-health/guide/weighing-your-toothpaste-options#1
- https://www.which.co.uk/reviews/electric-toothbrushes/article/choosing-the-best-toothpaste
- http://blog.deltadentalmn.org/are-all-toothpastes-the-same/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Toothpaste
- http://www.drinkbai.com/blog/why-juice-tastes-so-bad-after-you-brush-your-teeth
- https://dentalimplantsnewportnews.com/dental-implants-news/toothpaste-tooth-gel/
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12399689
- http://www.oralanswers.com/tag/toothpaste/
- www.dryasmin.ae
