Nonodontogenic Cysts
[divider scroll_text=””]
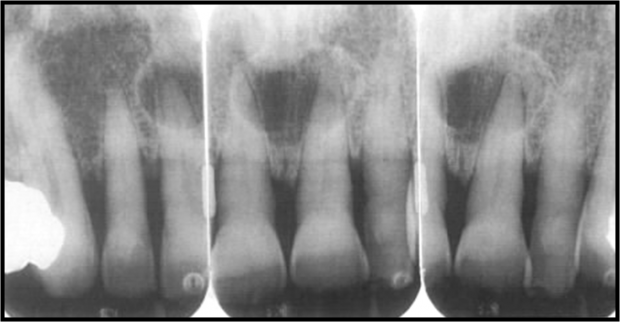
Nasopalatine cyst
Other Names
Nasopalatine canal cyst, Incisive canal cyst, Nasopalatine cyst, Median palatine cyst, Median anterior maxillary cyst
Definition
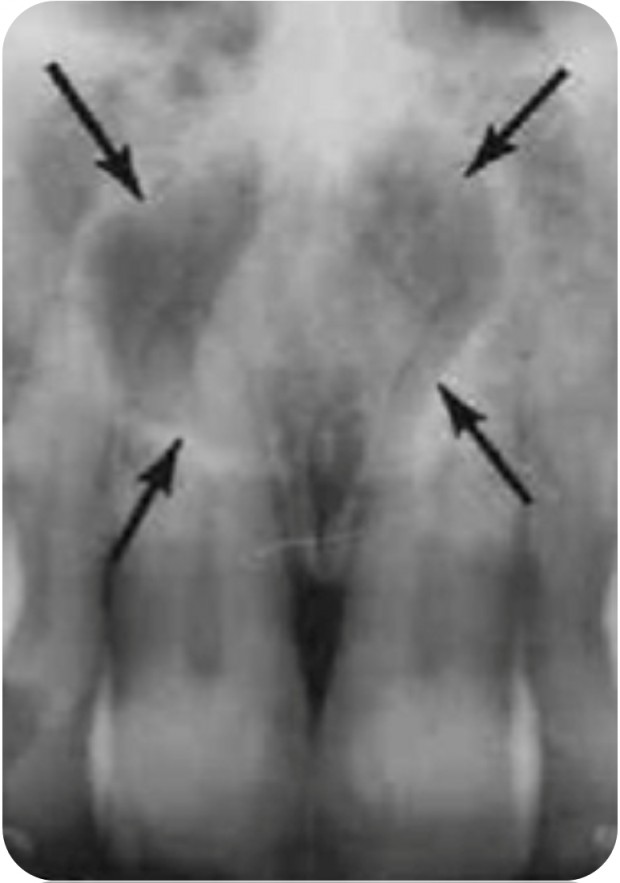
Is a developmental cyst derived from embryonic epithelial remanants of the nasopalatine duct. It usually contains a primitive organ of smell and both nasopalatine vessels and nerves.
Clinical Features
- It occurs in adult 4th to 6th decades.
- Occur more frequetly in men.
- It causes palatal swelling in the site of incisive papilla
- It may be symptomless or present as a slowly enlarging swelling in the front region of the midline of the palate. Occasionally it discharges into the mouth in which the person may complain of a salty taste. Pain may occur if the cyst becomes secondarily inflamed.
Radiography
- Location
Found in the nasopalatine foreman or canal. Depending on the location of expansion it has different variations.
- Periphery and Shape
Radiolucent
Well defined and corticated
Circular or oval in shape, but sometimes the nasal spine covers the cyst giving it a unique heart shape.
This cyst may not always be positioned symmetrically
- Surrounding structures.
Most cases the Cyst cause the roots to diverged or in some rarer case leads to root resorption.
Differential Diagnosis
- Incisive foramen
- A radicular cyst or granuloma associated with a central incisor
Treatment
Treated by enucleation.
[divider scroll_text=””]
Median Cysts
Features
- Its a variation of nasopalatine cyst, they are rare and occur in either the palate or the lower jaw.
- If this cyst extends posteriorly to involve the hard palate ,it often is referred to as a median palatal cyst.
- If it expands anteriorly between the central incisors, destroying or expanding the labial plate of bone and causing the teeth to diverge, it sometimes is referred to as a median anterior maxillary cyst.
Clinical Features
- Identical to nasopalatine cyst.
Treatment
- Identical to nasopalatine cyst.
[divider scroll_text=””]
Globumaxillary cyst
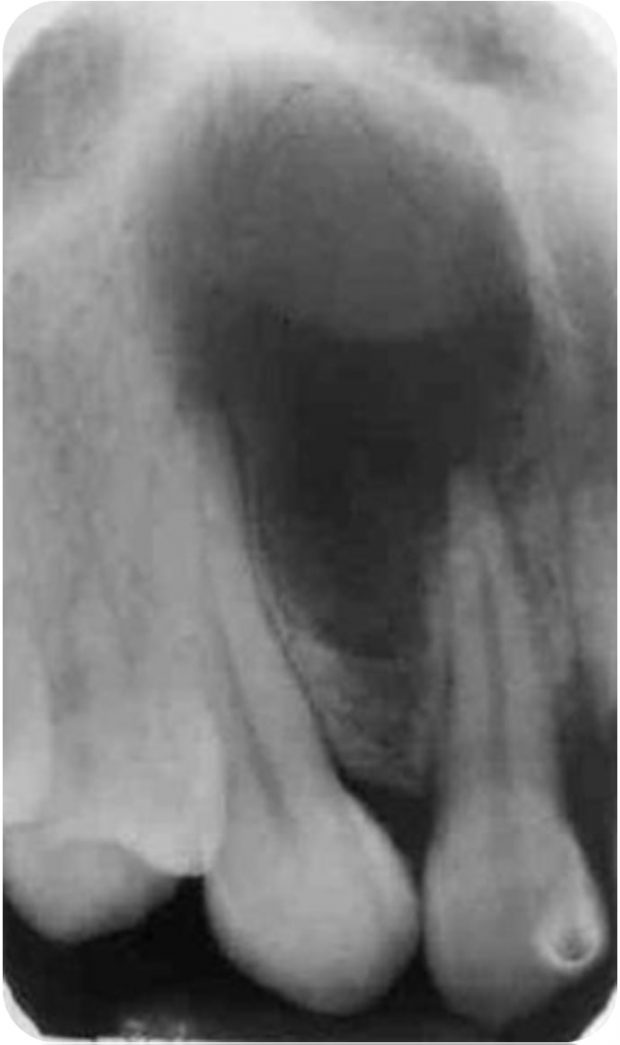
Definition
- Epithelium entrapment within a line of embryological closure with subsequent cystic change.
- located between globular and maxillary processes.
- Premaxilla and maxillary processes do not fuse.
Radiographically
- well-defined Radiolucent.
- The cyst often produces divergence of the roots of the maxillary, lateral incisor and the canine.
- It has a unique Inverted Pear Shape radiolucency
Treatment
- Treatment and prognosis are determined by definitive microscopic diagnosis.
[divider scroll_text=””]
Nasolabial cyst
Features
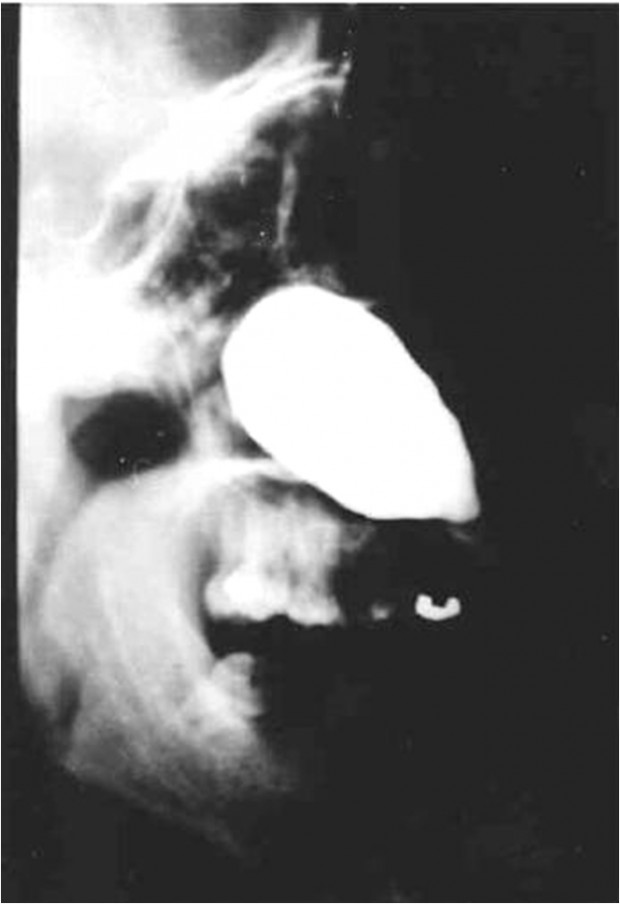
The nasolabial cyst is a rare lesion which arises in the soft tissue of the upper lip just below the ala of the nose. It has been suggested that it arises from remnants of the embryonic nasolacrimal duct. It is a Cystic change of the solid cord remnants of cells that form the nasolabial duct.
Clinical Features
- 4th to 5th decades.
- More in Female (4:1).
- Soft tissue swelling over the canine region or mucobuccal fold.
- No radigraphics changes in bone.
- It presents as a slowly enlarging soft tissue swelling obliterating the nasolabial fold and distorting the nostril.
- The cyst may arise on both sides of the face.
Treatment
- Curettage or surgical excision.
- Recurrence incidence isn’t common.
[divider scroll_text=””]
Sources
- Ibn Sina University Curriculum By Dr. M. Shanbari.
- Intelligent Dental by Dr. MEIFONG.
- Wikipedia.
OziDent Members Only
The rest of article is viewable only to site members,Please Register and/ or Confirm registration via EmailHere.If you are an existing user, please login.