It this article about failure of amalgam restorations, we will explain the etiology of the amalgam restored tooth fracture, clinical picture, causes, etiology and methods of treatment.
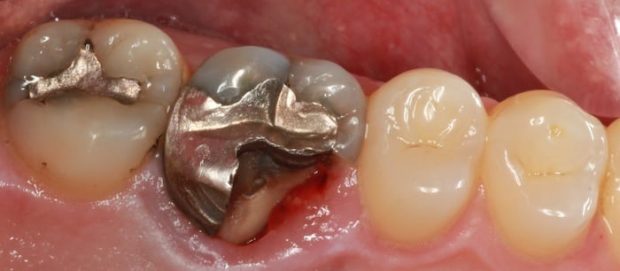
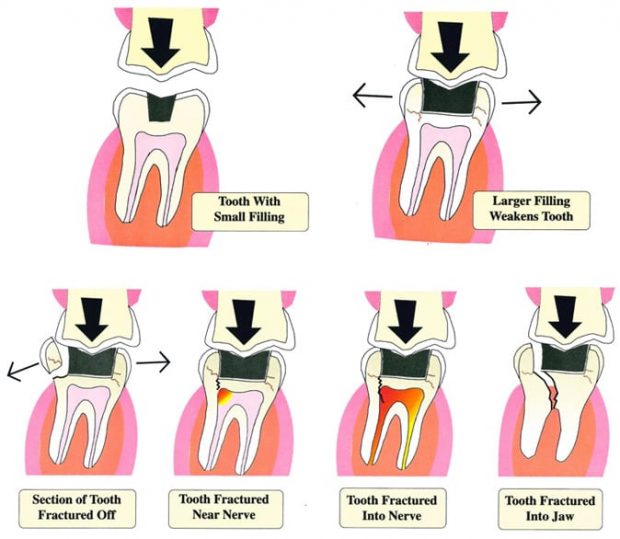
Tooth Fracture
Definition
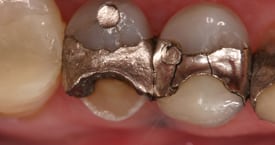
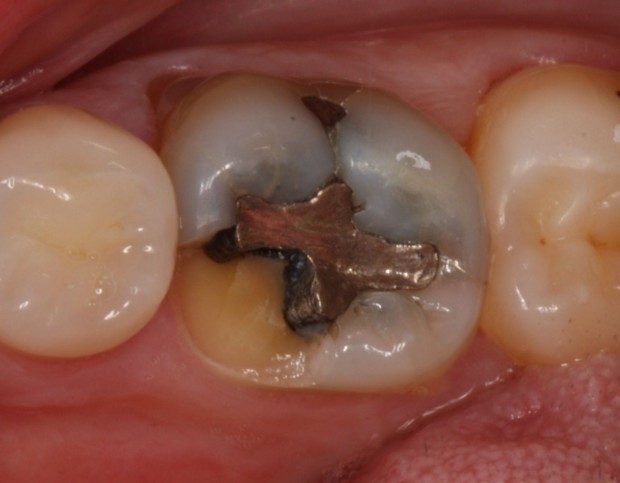
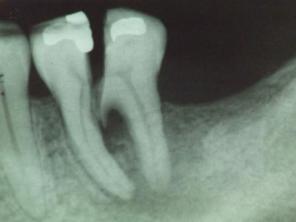
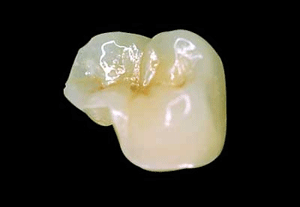
Fractured cusp or ridge under functional forces due to lack of support and reinforcement in the restored tooth.
[divider scroll_text=””]
[column col=”1/3″]
[/column][column col=”1/3″]
[/column][column col=”1/3″ last=”true”]
[/column]
[divider scroll_text=”S]
Etiology
Amalgam lacks sufficient tensile strength to support remaining tooth substance and much less able to re-enforce weak cusps and ridges. Thus it leads to a worst outcome if the restoration is relatively large leading to less support of remaining tooth structure.
Treatment
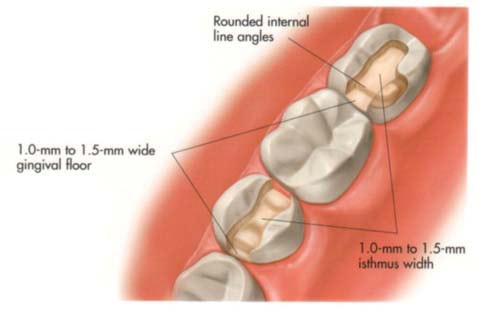
- Eliminate all undermined enamel as well as weak cusps and ridges.
- Preserve the integrity and continuity of the remaining tooth substance. Roundation of
- line angles.
- Ensure wide distribution of stresses.
- Reinforce weak cusps and ridges using inlays, onlays or full coverage.
[divider scroll_text=””]
[column col=”1/2″]
[/column][column col=”1/2″ last=”true”]
[/column]
OziDent Members Only
The rest of article is viewable only to site members,Please Register and/ or Confirm registration via EmailHere.If you are an existing user, please login.