In this Article, We will start with a basic Comparison between common types of Oral Ulcers. The comparison will be in the Etiology , on the preceding lesion before the ulcers occurs and Recurrence.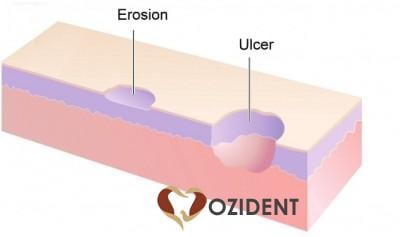
But first, we must understand what is an Ulcer.
Definitions
Ulcers: Is the complete loss of epithelium. Always Heals with a scar
Erosion: is a superficial damage leading to partial loss of epithelium. No Scar Formation
In The Comparison and previous image, the difference between an ulcer and erosion is quite easy to understand.
Comparison
By Etiology
| Etiology | Examples | |
| Physical or Chemical | Acid Burn, Heat Burn, Traumatic , Biting | |
| Microbial | Bacterial | Necrotizing Ulcerative Gingivitis, TB, Syphilis |
| Fungal | Histoplasmosis Blastomycosis | |
| Viral | Herpes Simplex, Herpes Zoster, Herpangina, Hand, foot and mouth disease | |
| Neoplasm | Squamous Cell Carcinoma | |
| Immunological reactions | Aphthous ulcers, Behcet’s syndrome, Pemphigus Vulgaris, Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid, Lupus Erythematosus, Lichen Planus, Epidermolysis Bullosa, Drug Eruption | |
| Blood disorders | Anemia, Leukemia, Neutropenia | |
| Gastrointestinal Disease | Coeliac Disease, Ulcerative Colitis, Crohn’s Diseases | |
| Drugs | Cytotoxic Drugs | |

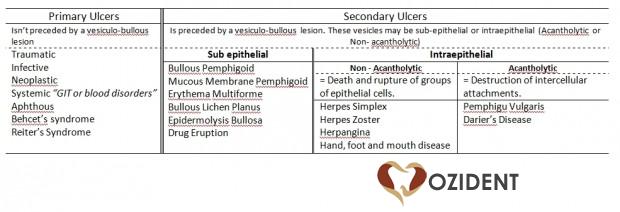
By Precursor Lesion
Primary Ulcers
- Definition: an ulcer that isn’t preceded by a vesiculobullous lesion
- Examples:
- Traumatic
- Infective
- Neoplastic
- Systemic “GIT or blood disorders”
- Aphthous ( The Most Common Oral Ulcers Read here about here)
- Behcet’s syndrome
- Reiter’s Syndrome
Secondary Ulcers
- Definition: an Ulcer that is preceded by a vesiculobullous lesion.
- Types: These vesicles may be sub-epithelial or intraepithelial (Acantholytic or Non- acantholytic)
[column col=”1/2″]
Sub Epithelial
- Bullous Pemphigoid
- Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid
- Erythema Multiforme
- Bullous Lichen Planus
- Epidermolysis Bullosa
- Drug Eruption
[/column]
[column col=”1/2″ last=”true”]
Intraepithelial
- Non – Acantholytic: Death and rupture of groups of epithelial cells.
- Examples:
- Herpes Simplex
- Herpes Zoster
- Herpangina
- Hand, foot and mouth disease
- Examples:
- Acantholytic: Destruction of intercellular attachments.
- Eamples:
- Pemphigus Vulgaris
- Darier’s Disease
- Eamples:
[/column]
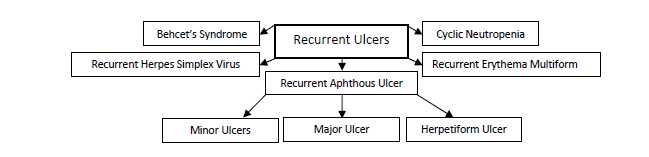
By Recurrence
OziDent Members Only
The rest of article is viewable only to site members,Please Register and/ or Confirm registration via EmailHere.If you are an existing user, please login.