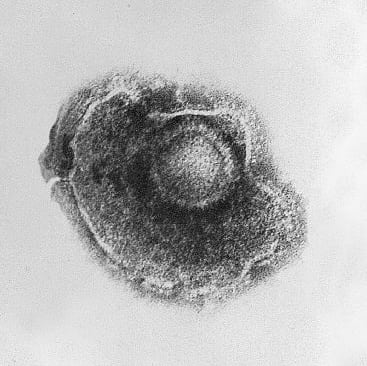
In this article, we explain the third form of human Herpes (HHV-3) in its primary form that causes oral ulcers, Varicella Zoster Virus.
Varicella Zoster Virus
Also Known as VZV, chicken pox virus, varicella virus, zoster virus, and human herpes virus type 3 (HHV-3).
HHV-3 also shares some ancestors with HSV1 and HSV2 while five genes do not have corresponding HSV genes. Relation with other human herpes viruses is less strong, but many homologues and conserved gene blocks are still found.
Facts
[column col=”1/2″]Varicella = Primary infection = Chicken pox [/column]
[column col=”1/2″ last=”true”]Zoster = Reactivate infection = Shingles.[/column]
- The same virus causes two different diseases.
- Varicella: In the Primary Infection (chicken Pox) the virus migrates from the epidermis via the Periaxon sheath of the sensory nerves and remains latent within either:
- Dorsal root ganglion of spinal cord.
- Extramedullary Ganglion of cranial nerves.
- Zoster: Once they are reactivated by predisposing factors (e.g. radiation, malignancy…etc)
- Zoster: The latent virus is triggered and spreads from the Ganglion to the nerve trunk to infect a specific dermatomes resulting in herpes zoster, this type of infection never occurs as a primary Infection.
[divider scroll_text=””]
Chicken Pox (Varicella)
A Common childhood fever (mild and febrile illness) due to primary infection with Varicella Zoster virus.
Transmission
- It invades the upper respiratory track by:
- Via Contaminated Droplets in the air.
- Via direct contact with fresh skin lesions of infected person either chicken pox or shingles.
[space height=”15″]
Incubation Period
- About 2 weeks (10 – 21 days)during which the virus proliferates within the macrophages.
- Then the Virus spreads and disseminates through blood (Viremia).
- Then Spreads to the skin, mucus membrane and other organs.|Age|
- At any age but the peak incidence is at 5 – 10 years.
- The disease is more severe in older children and debilitate (Weak) adults, while mild in younger children.
- Most common in spring and winter.
[space height=”15″]Clinical Features
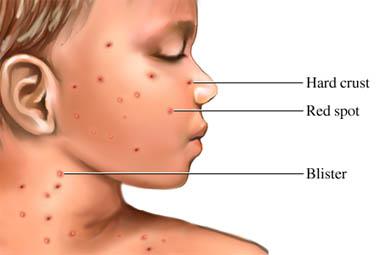
Prodrome
Mild fever, Headache and malaise.
Generally
- Vesicular rash in successive waves for 3 – 6 days, why? Due to repeated waves of viremia.
- Because of the successive waves the patient will have mixed skin lesions at the same time (Papules, vesicles, Pustules or crust).
- Fever subsides and new lesions will stop developing.
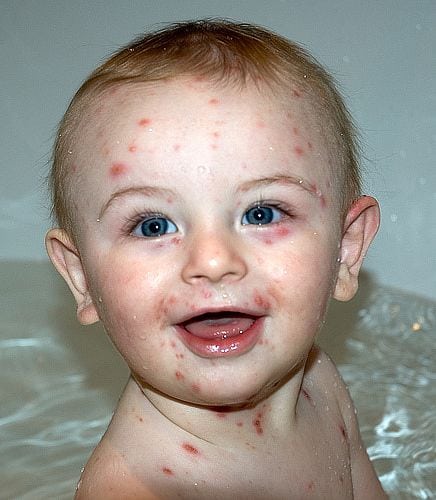
[space height=”15″]Extraoral Lesions
- Appears as a skin rash (Crops of red papules on the trunkspreads to the face, Scalp and extremities). These papules develop within hours into vesicles which appear clear like Tear drops.
- These Vesicles’ contents become Cloudydevelop into pustules.
- These Pustules rupturebecome scabbed and crusted.
Healing
- Heals with no scar formation unless 2nd infection.
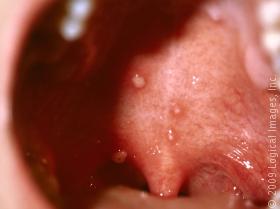
[space height=”15″]Intraoral lesions
- Appears as multiple vesicles, shallow, not painful ulcers. No symptomatic, diagnostic or treatment problems.
[divider scroll_text=””]
Treatment
Healthy children: no need for treatment, why? Because it’s self limiting disease.
- Less than 12 years old: 5 mg/kg every 8 hours for 7 days
- More than 12 years old: 10 mg/kg every 8 hours for 7 days
- Varicella zoster virus responds well to acyclovir but compared to herpes simplex less effective and because the Drug has low toxicity the dosage can be increased to get the needed effect.
Prophylaxis
- Passive immunization by ZIG (Varicella – Zoster Immunoglobulin) prepared from pooled plasma with high titres of Varicella – Zoster Antibody.
- Useful for prophylaxis and reducing the severity of the disease in vulnerable contacts of chicken pox or less often Herpes Zoster.
[space height=”15″]Vaccine
- Used in case of children with Leukemia or solid tumors as it provides good protection. It’s done by the use of an Alive Attenuated Virus Vaccine.
OziDent Members Only
The rest of article is viewable only to site members,Please Register and/ or Confirm registration via EmailHere.If you are an existing user, please login.