In this article, we explain the diffrent Velum positions that help perform the different plato-pharyangel mechanisms.
Plato-pharyngeal Mechanism
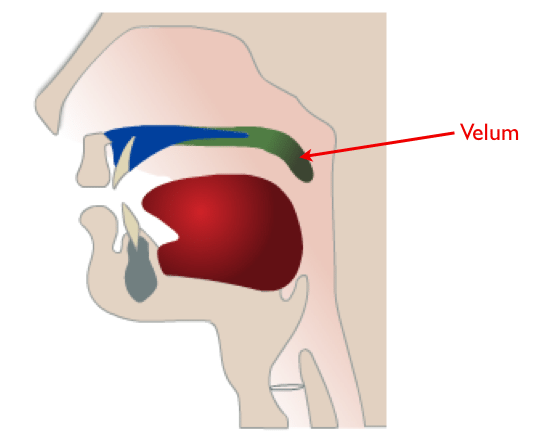
The Velum is The soft palate (also known as velum or muscular palate) is, in mammals, the soft tissue constituting the back of the roof of the mouth. The soft palate is distinguished from the hard palate at the front of the mouth in that it does not contain bone.[divider scroll_text=””]
Relaxed position of the velum
- Required for normal breathing from both the oral and nasal pathway.
- The velum is dropped downwards to keep the naso-pharynx and oro-pharynx opened.
Closures of the oral cavity
- Required to permit the exit of air through the nasal cavity for nasal breathing.
- Required during sucking.
- Required for pronunciation of sounds “M” and “Ng”
Mechanism
- Palato pharynges muscles pull the soft palate down towards the tongue.
- Tensore veli palatine muscles flattens the dome shaped of the soft palate.
- Palato glossus muscles contracts to force the tongue upward and backward.
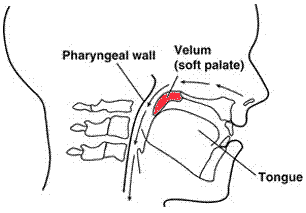
Closure of the nasal cavity
Required for swallowing and pronunciation of the letters in the oral cavity.
Mechanism
- Middle 1/3 of the velum is curved upwards and backwards contacting the posterior wall of the pharynx. It contacts at or above the plane of the plate at the level of the atlas vertebra.
- Done by Levator veli palatine muscle.
- Aided by the uvulae muscle to add bulk to the nasal surface of the velum.
- The closure isn’t completely done by the velum alone but the pharynx also accommodates by:
- Forward movement of the posterior wall of the pharynx (by the superior constrictor muscle and aided by the palate pharynges muscle).
- Lateral movement of the medially walls of the pharynx (by the Salpingo pharynges muscle)
- Strong Contraction of the posterior pharyngeal muscles to produce a prominent ridge called “Ridge of Passavant” which helps to approximate the soft palate with the pharynx. [divider scroll_text=””]
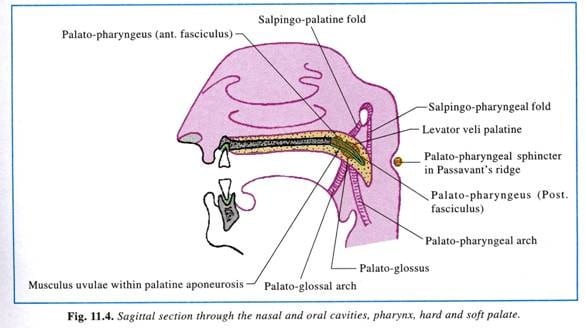
Ridge of Passavant
- Is a horizontal roll of tissue raised by fibers on the posterior wall of the pharynx forming prominence on the posterior wall of the pharynx, its located at the level of the plate (at the level of the atlas vertebra), Forms a ring around post and lat walls of nasopharyngeal isthmus.
- When soft palate is elevated the muscle band appear as a ridge
- More prominent in cases of soft palate defects with a compensating mechanism.
- Its considered a guide for placement of prophesies restoring palatal defects.
[divider scroll_text=””]
Plato-pharyngeal Defects
Plato pharyngeal insufficiency
Etiology: Inadequate / short length of the soft palate (due to congenital or developmental defects) leading to inadequate palate pharyngeal closure.
Plato pharyngeal incompetence
Etiology: normal tissue is present but with impaired function (due to neurologic disease “poliomyelitis” or cerebro vascular accidents) leading to inadequate palate pharyngeal closure.
Treatment: palatal lift prostheses.[divider scroll_text=””]
Sources
- Misr International University Prothesis Core curriculum.
- Wikipedia.
OziDent Members Only
The rest of article is viewable only to site members,Please Register and/ or Confirm registration via EmailHere.If you are an existing user, please login.