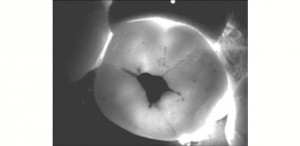
DiFOti (Digital Fiber Optic Trans-illumination)
Info
- Uses visible light not ionizing radiation.
- Its method is based on the fact that carious lesion scatters light, using this to distinguish the lesion from health enamel.
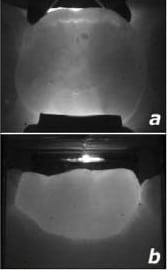
[tab]
[tab_item title=”Healthy Tooth”][/tab_item]
[tab_item title=”Caries on Tooth”]
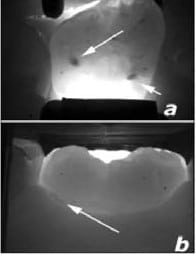
Arrow is pointed at the Areas that light is scattered, thus indicating a possible caries location.
[/tab_item]
[/tab]
- Light is passed through the tooth and collected by a camera and sent to a computer screen, then the image is displayed
- Detection of caries on proximal, smoot, occlusal surfaces and recurrent caries but cannot visualize sub gingival lesions (because light can’t reach it).
- Source of light for the inter‐proximal is from either the buccal or lingual surface with the camera on the opposite side. While in case of the occlusal surface the camera is placed on the occlusal side and light source is from both the buccal and lingual sides.
- The carious lesion appears dark compared the rest of the health tooth.
Components
The System Composes of:
- An instrument that contains both a light transmitter and a light receiver (camera).
- A display system to show the caries location.

[tab]
[tab_item title=”Camera 1″][/tab_item]
[tab_item title=”Camera 2″][/tab_item]
[tab_item title=”Computer”]

[/tab_item]
[/tab]
Advantages
- Has superior sensitivity over traditional radiography and can detect early lesion.
- Images is produced very fast as there is no need for processing.
- no Radiation is needed.
Disadvantages
- Difficult to distinguish carious lesion from enamel hypo‐mineralization and deeply stained fissures.
- Doesn’t show the depth of the lesion thus difficult to monitor the progress of any preventive regime.
- Diagnosis is completely based on the observer with no computer assistance.
OziDent Members Only
The rest of article is viewable only to site members,Please Register and/ or Confirm registration via EmailHere.If you are an existing user, please login.